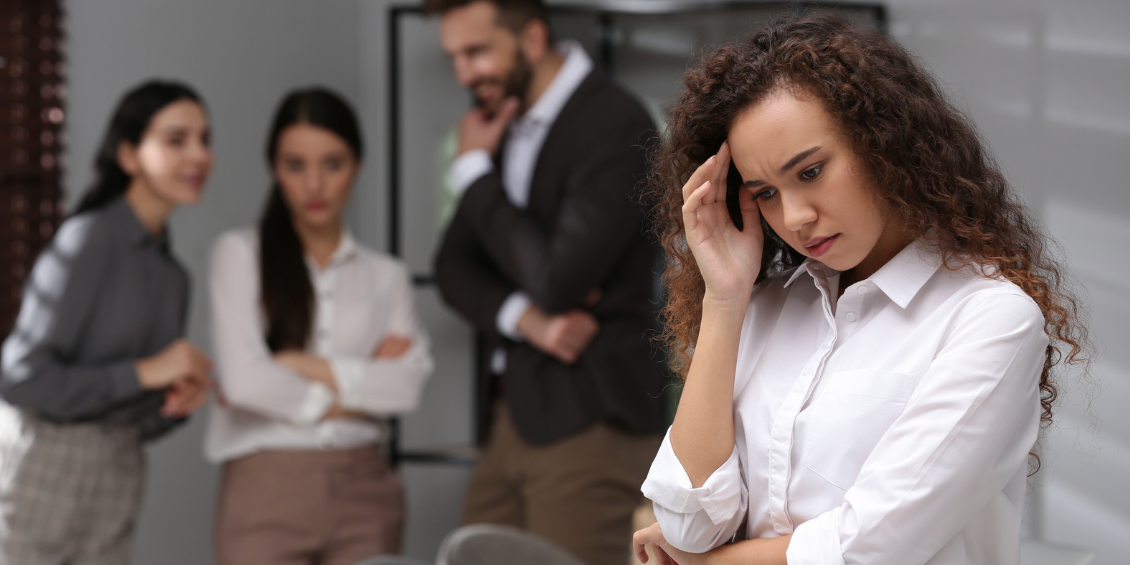
Age discrimination in the workplace remains a significant concern, affecting employees’ career growth, mental health, and overall well-being. Despite legal protections, many workers still experience ageism in various forms. Examples of age discrimination include unfair hiring practices, denial of promotions, age-based harassment, and forced retirement.
This comprehensive guide delves into the definition of age discrimination, explores examples, examines legal implications, and provides strategies for preventing and addressing this pervasive issue. This underscores the importance of organizations adhering to EEOC discrimination guidelines to foster an inclusive and equitable workplace for employees of all ages.
Understanding Age Discrimination
Definition of Age Discrimination
Age discrimination refers to the unfair treatment of individuals based on their age or age-related characteristics. This form of discrimination can occur in several employment-related decisions, such as hiring, promotions, job assignments, training opportunities, and layoffs. While age discrimination can affect both young and older workers, it predominantly targets older individuals.
The Age Discrimination in Employment Act (ADEA)
In the United States, the primary federal law addressing age discrimination is the Age Discrimination in Employment Act (ADEA), enacted in 1967. The ADEA prohibits age discrimination against individuals who are 40 years of age or older. It applies to employers with 20 or more employees, including state and local governments, and protects employees and job applicants from age-related discrimination in all aspects of employment.
Protected Age Group
The ADEA specifically protects individuals who are 40 years of age or older. However, some states have laws that provide broader protection, covering employees of all ages. These state laws aim to prevent any form of age discrimination, recognizing that younger workers can also face bias.
Examples of Age Discrimination
Age discrimination manifests in various forms within the workplace. Understanding these examples can help victims identify and address unfair treatment.
Unequal Treatment in Hiring
Age discrimination can occur during the hiring process when employers favor younger candidates over older ones. Job advertisements may use language that implies a preference for “recent graduates” or “digital natives,” excluding older individuals who possess the necessary skills and experience. Employers might also ask inappropriate age-related questions during interviews, such as asking for graduation dates or inquiring about retirement plans.
Promotion Denial Based on Age
Older workers may be overlooked for advancement opportunities despite their qualifications and experience. Employers might assume that older individuals are less adaptable to change or lack the necessary skills for higher-level positions. This type of discrimination can hinder career growth and limit professional development opportunities for older employees.
Age-Based Harassment
Age-based harassment involves unwelcome comments, jokes, or derogatory remarks targeting an individual based on their age. Such behavior creates a hostile work environment and can negatively impact an employee’s mental and emotional well-being. Examples include derogatory comments about an employee’s appearance, physical abilities, or outdated stereotypes about older workers.
Disparate Impact on Older Workers
Disparate impact occurs when an employment policy or practice appears neutral but disproportionately affects older workers. For instance, implementing a mandatory retirement policy or setting arbitrary age limits for certain job positions can result in the exclusion of older employees who are capable and willing to continue working. These policies perpetuate age-related stereotypes and deny older workers equal employment opportunities.
Read Also : Maceo Robert Martinez: The Untold Story of Halle Berry’s Youngest Child
Forced Retirement
Forced retirement refers to the practice of requiring employees to retire at a specific age, regardless of their performance or desire to continue working. The ADEA prohibits mandatory retirement for most employees, except for certain high-level executives or public safety personnel. However, some employers still enforce such policies, perpetuating age discrimination.
Decreased Training Opportunities
Older employees often receive fewer training opportunities compared to their younger colleagues. This can limit their ability to stay updated with industry trends and advancements. Employers might assume that investing in older employees’ training is not worthwhile, thereby hindering their career progression and professional development.
Unequal Pay
Age discrimination can also manifest as pay disparity. Employers may pay younger employees less than older workers in senior positions, regardless of qualifications or performance. Conversely, older employees might face salary reductions or be denied raises that their younger counterparts receive, based solely on age.
Isolation from Team Activities
Age discrimination can lead to social isolation in the workplace. Older employees might be excluded from important meetings, team-building activities, or informal gatherings, which can affect their sense of belonging and professional relationships.
Legal Implications of Age Discrimination
Understanding the legal framework surrounding age discrimination is crucial for victims and those who wish to support them.
ADEA Protections and Enforcement
The ADEA prohibits employers from discriminating against individuals who are 40 years of age or older in any aspect of employment. It applies to private employers with 20 or more employees, state and local governments, employment agencies, and labor organizations. Employees who have experienced age discrimination may be entitled to remedies such as back pay, reinstatement, promotion, reasonable accommodation, and compensatory damages for emotional distress.
Filing an Age Discrimination Complaint
Employees who believe they have been victims of age discrimination can file a complaint with the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC), the federal agency responsible for enforcing the ADEA. The EEOC investigates complaints and, if appropriate, may file a lawsuit on behalf of the aggrieved employee. Generally, employees must first file a complaint with the EEOC and receive a right-to-sue letter before pursuing a lawsuit.
Case Studies: Real-Life Examples of Age Discrimination
Age Discrimination in the Tech Industry
In the tech industry, age discrimination is prevalent. Older workers often face challenges securing employment due to stereotypes associating technical proficiency with youth. In a prominent case, an experienced software engineer in his late 50s claimed he was repeatedly passed over for job opportunities at a well-known tech company in favor of younger candidates. The employee alleged that interviewers asked age-related questions and made comments indicating a preference for younger employees. Eventually, he filed an age discrimination lawsuit against the company, alleging violations of the ADEA.
Age Discrimination in the Healthcare Sector
Age discrimination affects various sectors, including healthcare. In a notable case, a registered nurse in her early 60s alleged that she was denied a promotion to a nursing supervisor position in favor of a younger, less experienced nurse. The nurse claimed that her supervisor made derogatory comments about her age, stating that she was “too old to handle the responsibilities” of the position. She filed a complaint with the EEOC and ultimately reached a settlement with the healthcare facility.
Prevention and Addressing Age Discrimination
Preventing and addressing age discrimination requires a multi-faceted approach involving both employers and employees.
Promoting Age Diversity and Inclusion
Employers should actively promote age diversity and inclusion within their organizations. This can be achieved by implementing policies that prohibit age discrimination, fostering inter-generational collaboration, and valuing the contributions of employees of all ages. Recruitment and hiring practices should reflect age diversity.
Educating Employees and Management
Education is crucial in combating age discrimination. Employers should provide training to employees and management on the importance of age diversity, the negative impact of age discrimination, and strategies for promoting an inclusive workplace. Training sessions can focus on identifying and addressing age-related biases, creating awareness of age discrimination laws, and fostering empathy and understanding among employees.
Creating a Fair and Inclusive Workplace Culture
Employers should cultivate a workplace culture that respects and values employees of all ages. This can be achieved by promoting open communication, providing equal opportunities for professional development, and recognizing the diverse skills and experiences that employees of different age groups bring to the table. Clear policies should be in place to address age discrimination complaints and ensure that employees feel safe and supported when reporting incidents of discrimination.
Advantages of Age Diversity in the Workplace
While age discrimination is a significant issue, it is essential to recognize the advantages of age diversity in the workplace. Embracing employees of all ages can lead to numerous benefits for organizations.
Experience and Wisdom
Older employees bring a wealth of experience and wisdom to the workplace. Their years of professional experience can provide valuable insights and knowledge, contributing to better decision-making and problem-solving. The mentorship and guidance that older employees can offer to younger colleagues can foster professional growth and development.
Inter-Generational Collaboration
A diverse workforce that includes employees of different ages promotes inter-generational collaboration. By bringing together individuals with varying perspectives, skills, and experiences, organizations can foster innovation and creativity. Different generations can learn from one another, exchange ideas, and contribute to a more dynamic and productive work environment.
Innovation and Creativity
Age diversity in the workplace can fuel innovation and creativity. Older employees often possess a deep understanding of industry trends and historical contexts, while younger employees may bring fresh perspectives and technological expertise. By harnessing the collective knowledge and creativity of employees of all ages, organizations can drive innovation and remain competitive in a rapidly evolving business landscape.
Conclusion
Age discrimination is a deeply concerning issue with far-reaching effects on individuals and society as a whole. It is imperative that organizations and employees work together to prevent and address age discrimination in the workplace. By fostering age diversity, promoting inclusivity, and understanding the legal implications surrounding age discrimination, we can create fair, equitable, and thriving work environments that value employees of all ages. If you believe you have a valid age discrimination claim, seeking legal representation from an experienced employment attorney is crucial. They will guide you through the legal process, advocate for your rights, and help you secure the compensation you deserve. Together, we can create a more inclusive and equitable work environment for employees of all ages.